How many people are living in the world today? Where do most of them live?
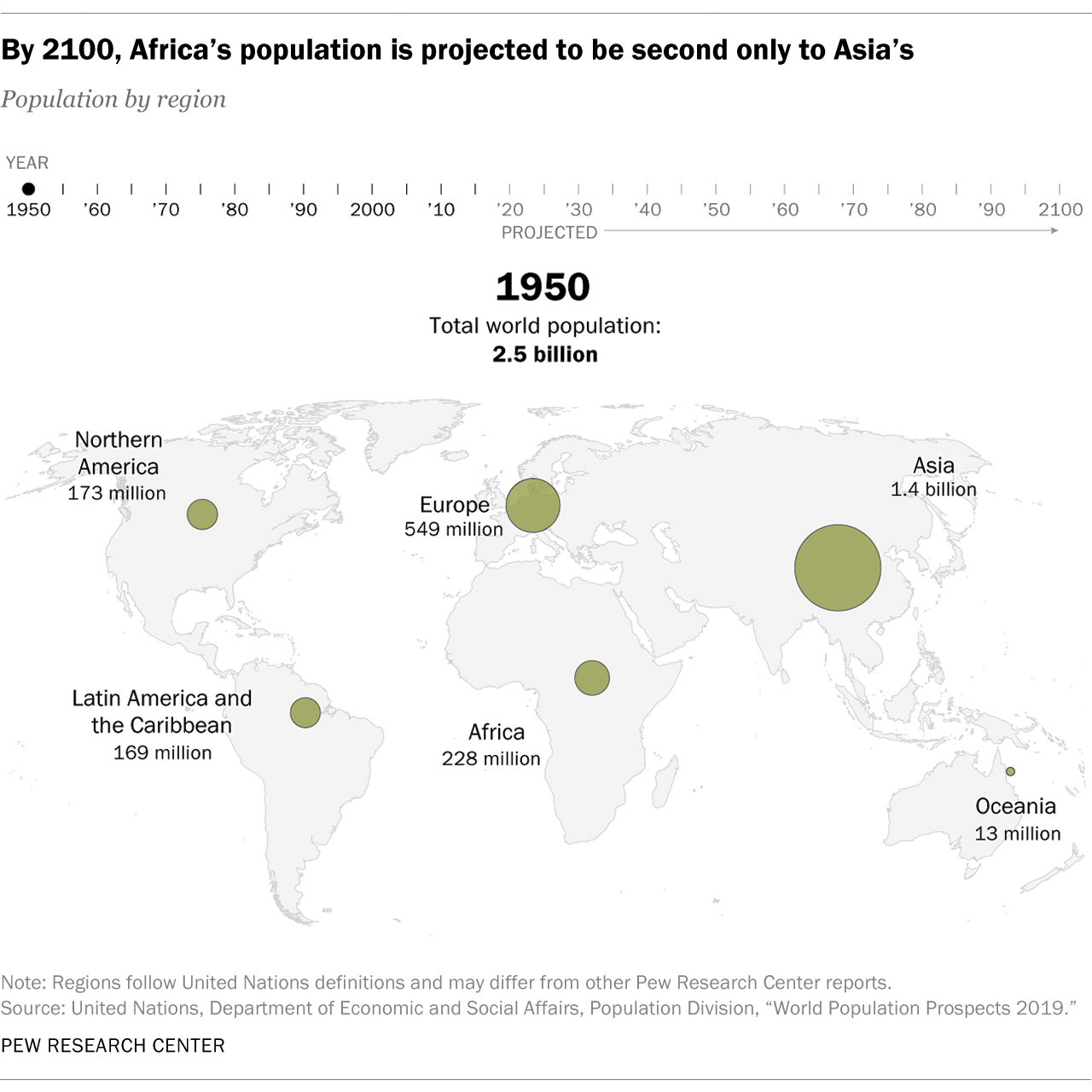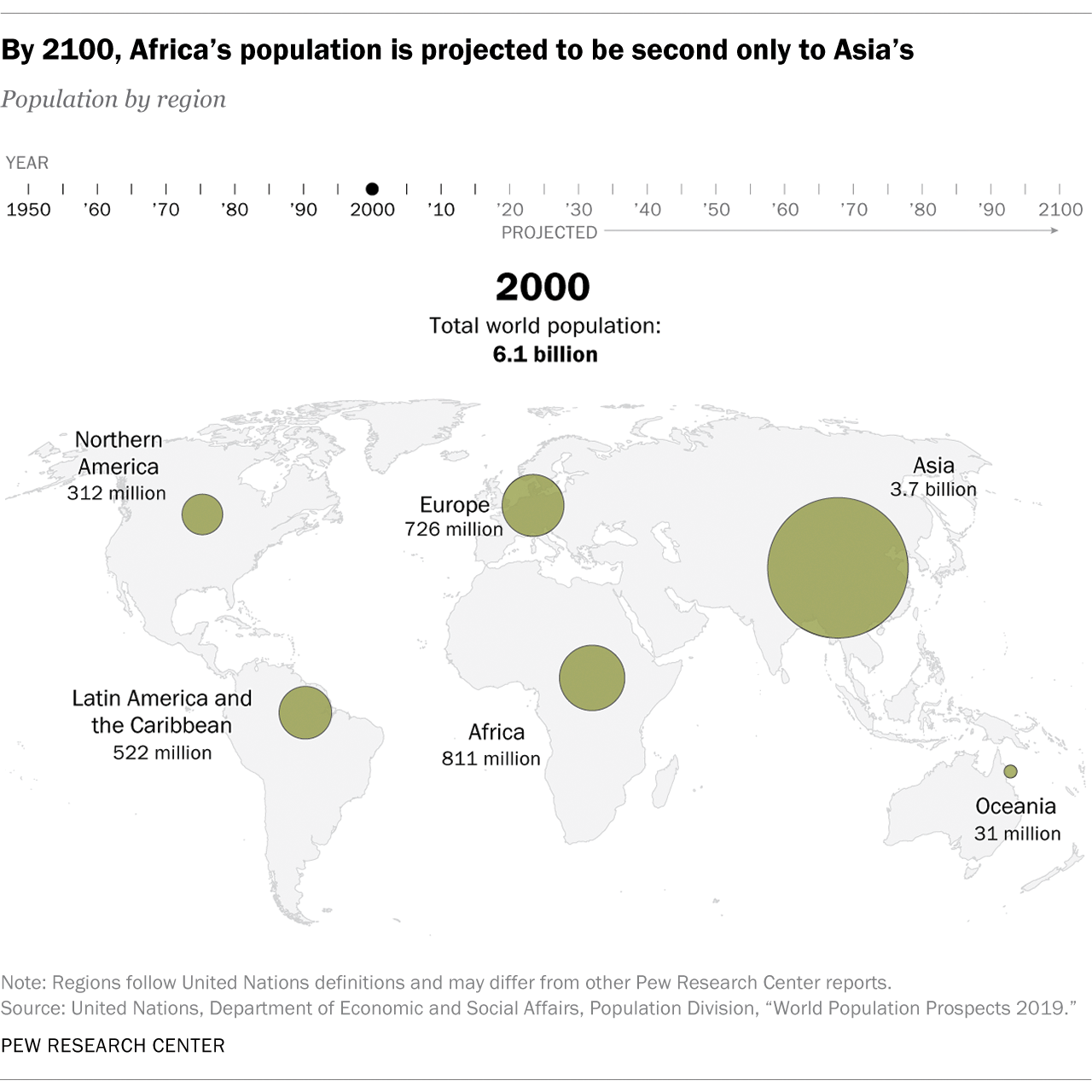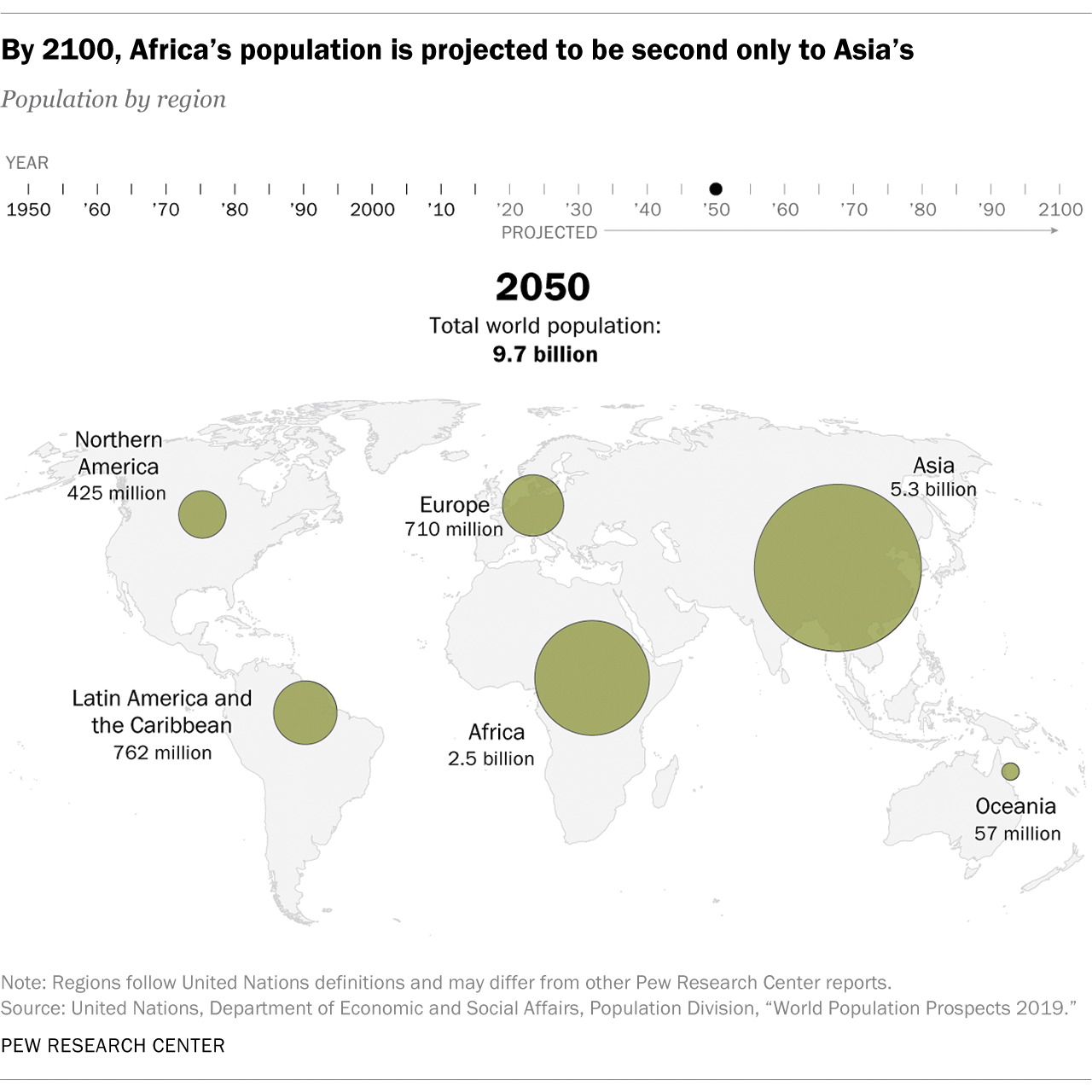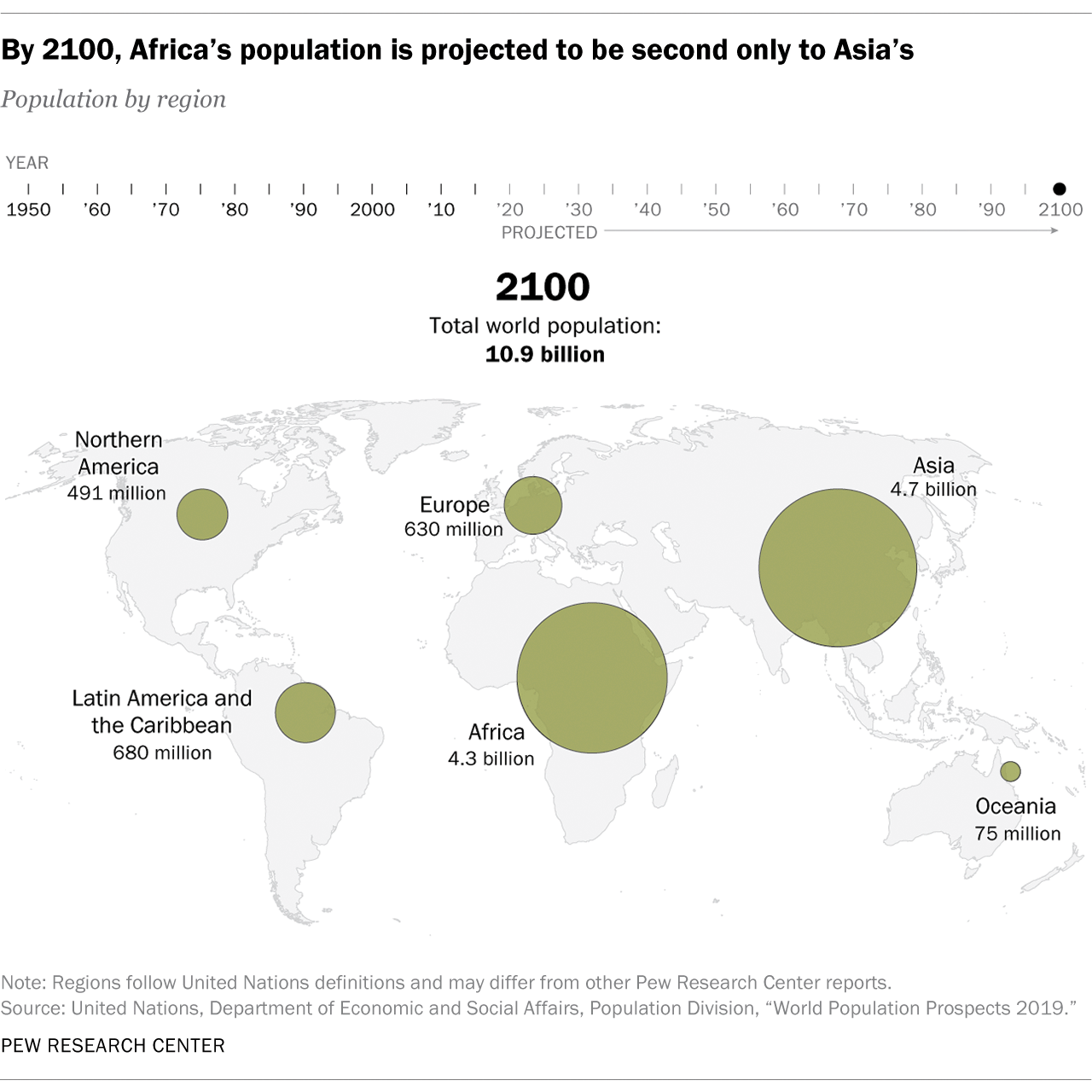
There are currently around 7.8 billion people in the world based on the estimates of the United Nations (UN).
This figure is rapidly rising. By 2100, projections place the size of the world population at nearly 11 billion.
Which are the most populous countries on Earth today?
Highlights
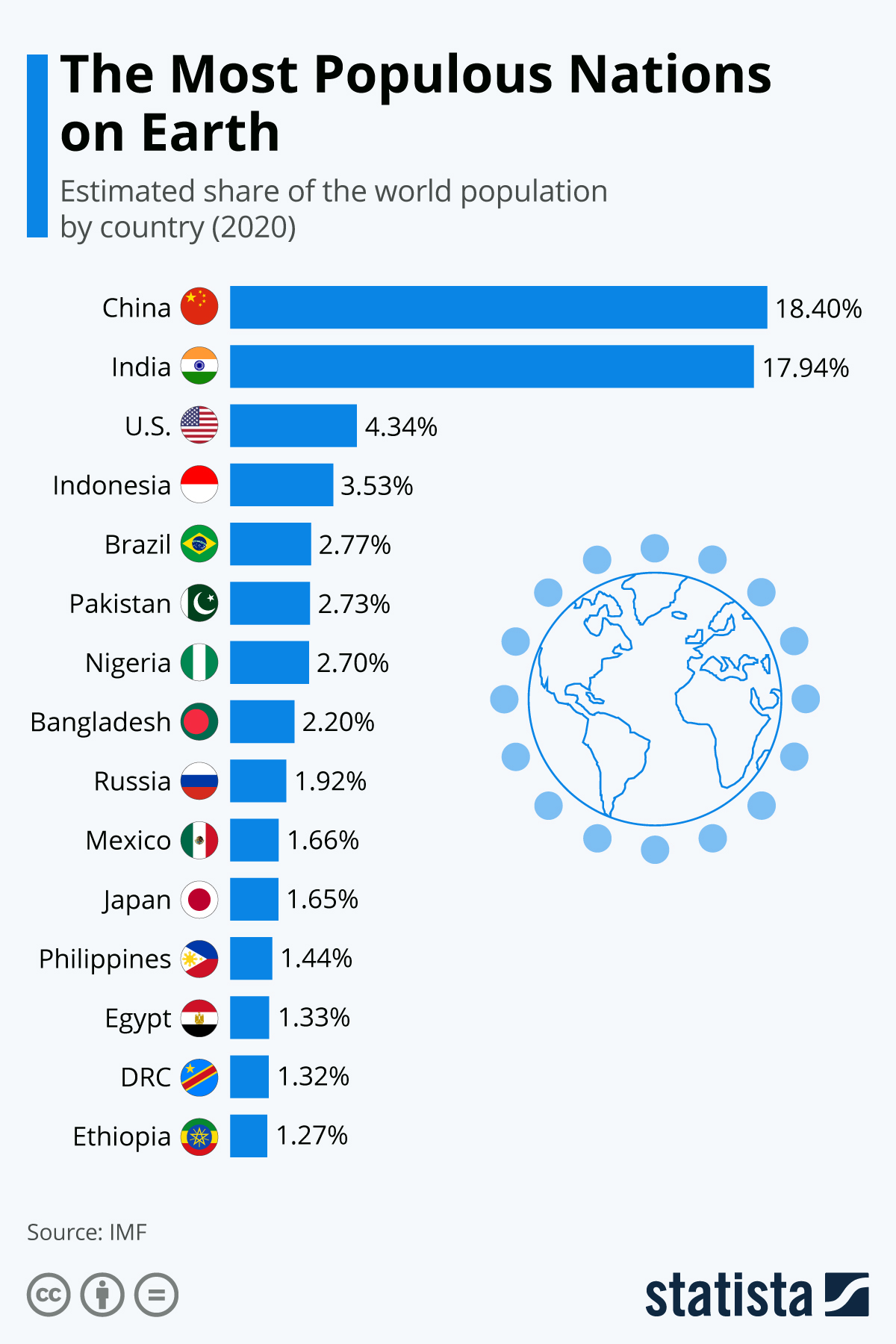
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), most of the people in the world today live in China. More than 1.43 billion or 18.40% of the population reside in the nation which is also the fourth largest in terms of landmass.
A close second is China’s geographic neighbour, India, where approximately 1.40 billion (17.94%) of the global population originated from. Together, these two countries account for more than a third of the current global population. Based on UN projections, however, India is set to overtake the population of China by the year 2027. This is due to an impending population decline in China driven by a strict one-child policy implemented in the country for years before it was eased to a two-child restriction in 2016.
In third place is the United States, with nearly 340 million inhabitants. The main driver of population expansion in the U.S. is immigration. By 2100, the country is expected to go down by one rank as it will be overtaken by the quickly rising population of Nigeria which is only at the seventh place today. Indonesia (3.53%) and Brazil (2.73%) occupy the fourth and fifth positions. The top five collectively account for almost half of the world’s population today.
Most of the largest countries in terms of population size are located in Asia. Within the top 15, seven countries are in this continent: China (1st), India (2nd), Indonesia (4th), Pakistan (6th), Bangladesh (8th), Japan (11th), and the Philippines (12th).
Populations prospects
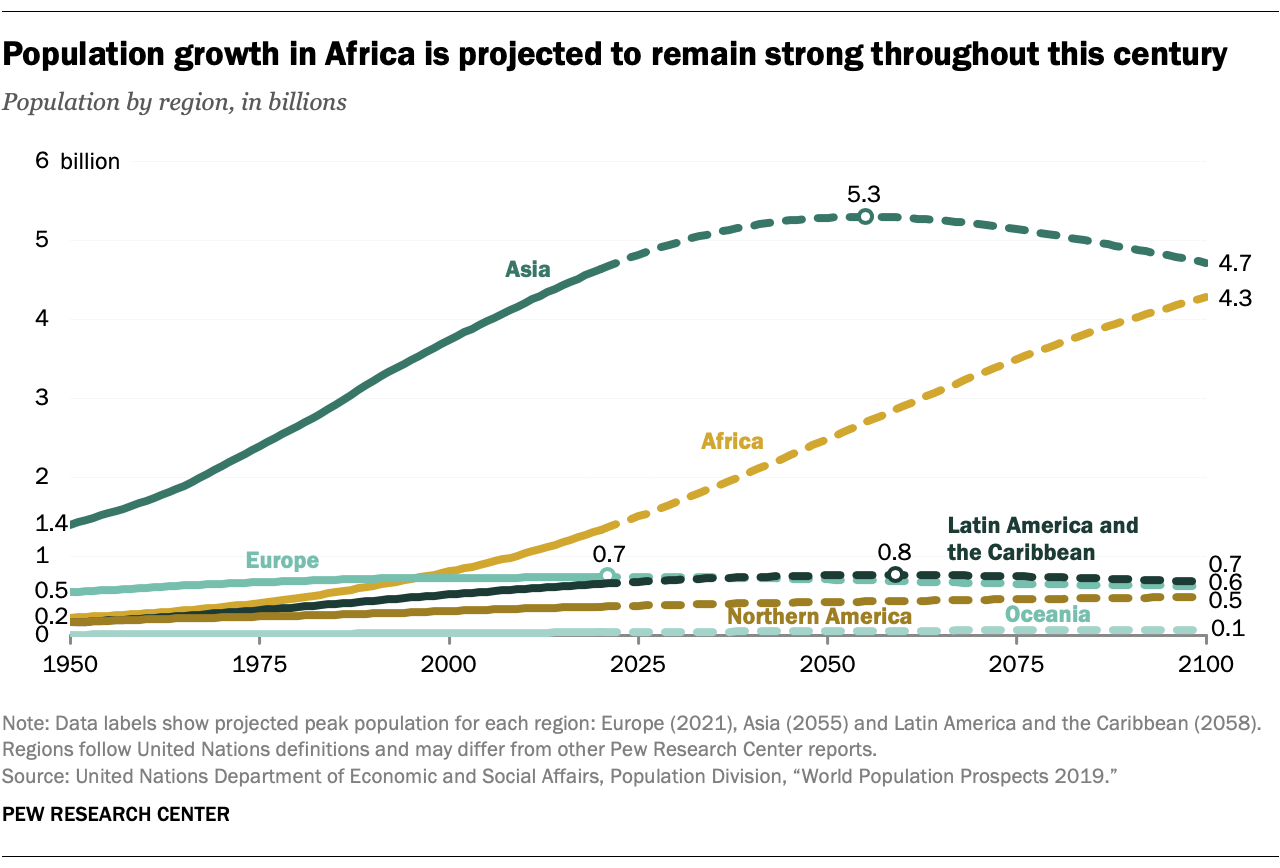
Even by the end of the century, projections expect Asia to remain as the world’s most populated region According to the UN projections, however, Asia will begin to experience decline by as early as 2055.
On the whole, the UN anticipates that 90 countries will face population losses between 2020 and 2100. There are two main factors contributing to this decline: sustained low levels of fertility and — for some areas — high rates of emigration.
On the other hand, Africa’s population will continue to expand quickly throughout the century. It is the only region that is expected to sustain a strong growth trajectory within this period. This will allow it to reach a population of 4.3 billion by 2100, closing in with Asia’s projection of 4.7 billion.
Africa’s growth is attributed to a high estimated number of births. By 2060, half of the babies that are born in the world are expected to be born in the continent.
The UN pointed out that most of the population growth that we would undergo in the years to come would come from the poorest countries in the world. With this, they highlighted the importance of adapting to demographic realities and ensuring inclusive population growth by incorporating population trends in government policies and plans.