The big idea: It’s the enduring media image of infectious disease outbreaks, including the current coronavirus outbreak from Wuhan, China: people in public spaces with faces half-hidden by surgical masks.
Filters have long been used to remove particles, including viruses and bacteria, from the air we breathe. Particle filters are key components of building and aircraft ventilation systems. Unfortunately, viruses are much smaller than the smallest particles those filters typically capture reliably.
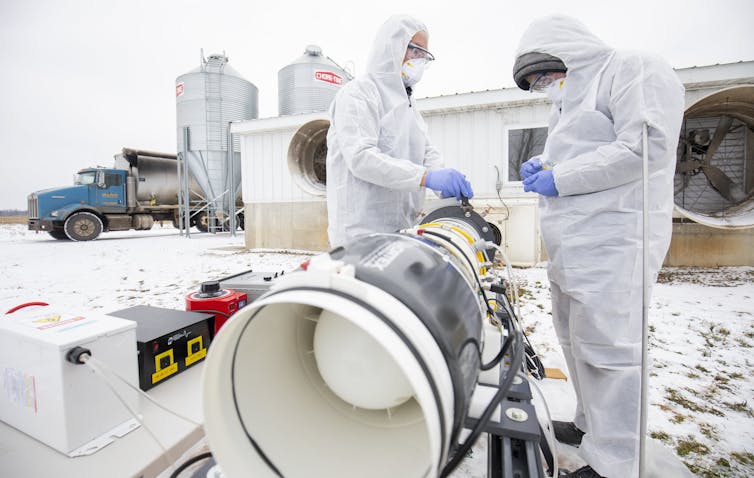

One possibility for curbing the spread of airborne pathogens is a nonthermal plasma reactor. Plasma is the fourth state of matter, a gas composed of electrically charged ions and electrons rather than neutral atoms and molecules. Nonthermal means the plasma isn’t formed at high temperatures. At the University of Michigan, my colleagues and I developed a nonthermal plasma reactor that leaves airborne pathogens unable to infect host organisms, including people. The plasma oxidizes the viruses, which disables their mechanism for entering cells.
After testing in the lab and at livestock facilities, we’ve shown that the reactor reduces the numbers of infectious viruses in an air stream by more than 99%. We’re developing the technology for use in animal agriculture, but it might also be useful where people are concentrated in enclosed spaces, including commercial aircraft.
Why it matters
Scientists don’t know what makes some viruses and bacteria more resilient in air than others. Tuberculosis and measles have long been known to be highly contagious, while a recent study proved that influenza can also remain infectious in air longer than an hour, something that researchers had previously thought unlikely. Enclosed or crowded spaces reduce opportunities for virus degradation or dilution in air, increasing the chances that an exposure will lead to infection.
Infectious diseases that have airborne transmission routes, including swine flu and avian flu, have affected pork, poultry and egg producers. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome alone has been estimated to cost more than US$600 million annually in the U.S. In 2015, more than 50 million chickens and turkeys were culled to stop the spread of highly pathogenic avian flu because of its potential to infect humans.
What we don’t know
There are several theories of how nonthermal plasmas kill bacteria, but airborne viruses aren’t “alive” like bacteria and therefore can’t be “killed” in the same way. Also, researchers’ understanding of nonthermal plasma sterilization is mostly based on sterilizing contaminated surfaces using minutes-long plasma exposures, much longer than the subsecond exposures studied in our tests and an earlier similar study.
In our tests, the plasma reduced how many infectious viruses were in the air by more than 99%, but the viruses themselves remained with their DNA largely unchanged. This means that the plasma didn’t destroy the virus but rather altered its ability to infect. We’re working to understand how this happens, which will help us engineer, or “tune,” the reactor.
What’s next
My colleagues and I are currently evaluating how ammonia, ever-present around animals as a byproduct of their waste, affects the plasma generated by the reactor.
We’re also considering how to use nonthermal plasma reactors in aircraft. Long-distance flights can transport infected passengers all over the world, as is immediately clear from maps showing confirmed cases of the new coronavirus. Less clear is the risk to fellow passengers. There are many aspects of virus transmission in aircraft cabins, including passenger movement during flights. Cabin air circulation patterns are important in determining how far and where a virus can be transported once shed by an infected passenger.
Scientists will need to better understand these variables before aircraft makers and operators can use nonthermal plasma reactors to help fight the spread of infectious diseases.
![]()
Herek Clack, Associate Professor of Civil & Environmental Engineering, University of Michigan
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.