Most people think or at least hope their government is doing a good job in the face of COVID-19, according to the polls. But there can be no doubt that governments around the world were ill-prepared for this pandemic.
Country after country has been locking their citizens in their homes to slow the spread of the virus for fear that their health systems get overwhelmed, as has happened in Italy. The lack of ventilators and protective equipment are a particular problem, despite the fact that scientists have called for years for governments to stockpile these life-saving machines and protective equipment.
How is it possible that we were not ready? Not only had Bill Gates been banging on about this for a long time, but pandemics also featured strongly on regional and national risk registers produced by governments and bureaucrats, as well as international registers from non-governmental organisations. These administrative tools, highlight the most likely and impactful events that could befall societies, from earthquakes to terrorism, and including influenza and novel pandemics.
Despite all the effort that has gone into developing these tools, governments around the world have been bad at acting on their warnings about a pandemic. We see at least six possible reasons for this.
First, some policymakers, at least in the west, did not believe the magnitude of the problem. This was because comparable events were beyond memory, like the 1918 “Spanish” flu; or were not that severe, like Sars, bird flu and swine flu. Even Ebola was contained and subdued with relative ease, other than in west Africa where it originated. There was a sense that modern medicine, at least in advanced countries, could cope with anything the microbiotic world threw at it.
Second, some sceptical politicians and the commentators they listen to thought that risk analysts and scientists cried wolf over past viral threats like swine flu and bird flu, and thought some of the risks seemed overstated or even incredible. It does not help that pandemics often appear on the same graphs as issues like space weather, which, while a real and pressing issue, is not widely understood and sounds like something out of a Star Trek episode.
Third, because electoral cycles are short, politicians tend to focus more on the short term. This is a common human trait, but the ramifications are more severe for politicians. Areas of public policy that require long-term investment, especially intangibles such as disaster planning, tend to be lower priority. Politicians either think that the public does not know about the risks or that they do not care.
Fourth, as a species we are good at rewarding people who fix problems, but terrible at acknowledging a problem averted. For example, former US Transport Secretary Norm Mineta received much praise for insisting that cockpit doors should be bulletproof after 9/11. How much praise would he have received if he had done it before 9/11? Consequently, government interest tends to focus on events that have already occurred such as floods or earthquakes.
Fifth, risk registers are confusing. They can feature an overwhelming amount of information, including long lists of many hazards and risks, and large scatter graphs like the one below linking the likelihood of an event with its impact. The illusions of comprehensiveness, precision and control can lull readers into a false sense of security. But given that the registers are calculated using many assumptions, they can also be seen as inherently speculative, hypothetical and even discountable to politicians.
Global risks in 2020
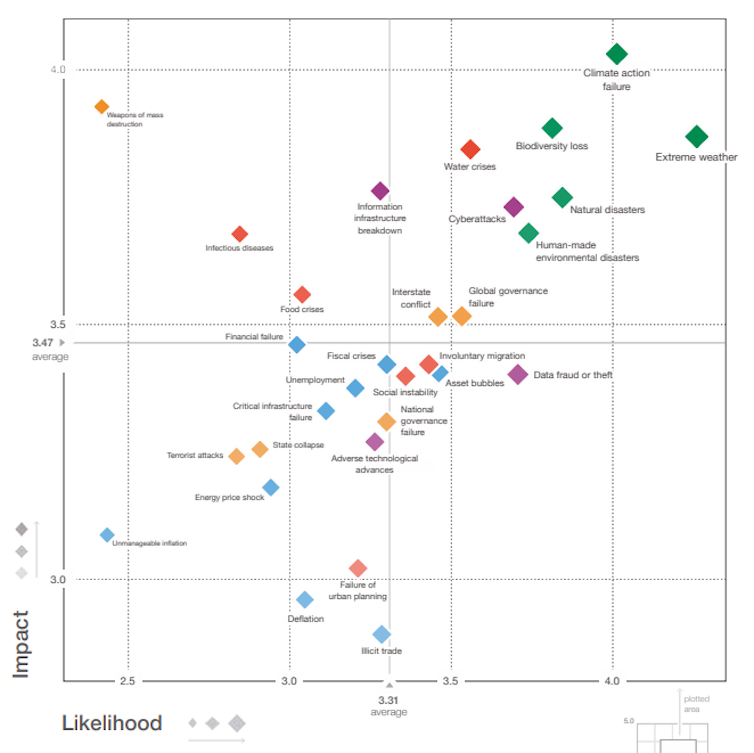
Sixth, risk registers, if taken as providing guidance and accountability, can become politically risky if an event happens and governments have not been prepared. This is why some countries, for example New Zealand, have not published their risk registers despite the obvious value of developing a common understanding about risks and helping various societal sectors to prepare for them. Those that don’t publish their registers come under less pressure to act on them.
What to do next time
Given all these problems, what could be done differently to make sure we are better prepared for such crises in future?
To start with, risk registers need to be produced largely outside the political process through a partnership between experts and policymakers. But they should also involve input from a diverse range of groups, for example indigenous people or key workers, so their interests are included in both identifying risks and planning responses.
Each country needs to understand and learn from how others are analysing, planning and have dealt with similar emergencies in the past. It is worth noting that parts of the world most affected by Sars appear to have handled the current pandemic with more urgency and success.
Risk registers should also be published to build trust and consensus in government preparations. This would also allow sections of society, including local government, businesses, charities and individuals, to take their own appropriate actions.
However, registers should not be seen as an end in themselves but rather as live documents against which governments and agencies constantly test themselves to make sure that they are doing enough. Practice trials, as happen in the UK, are essential but need to be followed up with action to improve future responses. Simply acknowledging that we are not prepared for a pandemic is not enough.
![]()
Chris Tyler, Associate Professor in Science Policy and Knowledge Infrastructure, UCL and Peter Gluckman, Director of Koi Tū, the Centre for Informed Futures; former Chief Science Advisor to the Prime Minister of New Zealand
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.